Top Essay Writers
Our top essay writers are handpicked for their degree qualification, talent and freelance know-how. Each one brings deep expertise in their chosen subjects and a solid track record in academic writing.
Simply fill out the order form with your paper’s instructions in a few easy steps. This quick process ensures you’ll be matched with an expert writer who
Can meet your papers' specific grading rubric needs. Find the best write my essay assistance for your assignments- Affordable, plagiarism-free, and on time!
Posted: December 21st, 2023
Table of Contents
We hear “Can you write in APA or MLA?” all the time—and the answer’s a big yes, plus way more! Our writers are wizards with every style—APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Turabian, you name it—delivering flawless formatting tailored to your assignment. Whether it’s a tricky in-text citation or a perfectly styled reference list, they’ve got the skills to make your paper academically spot-on.
1.3 Geographic and Demographic
1.3.1 Past & Current Population
Yes, completely! They’re a valid tool for getting sample papers to boost your own writing skills, and there’s nothing shady about that. Use them right—like a study guide or a model to learn from—and they’re a smart, ethical way to level up your grades without breaking any rules.
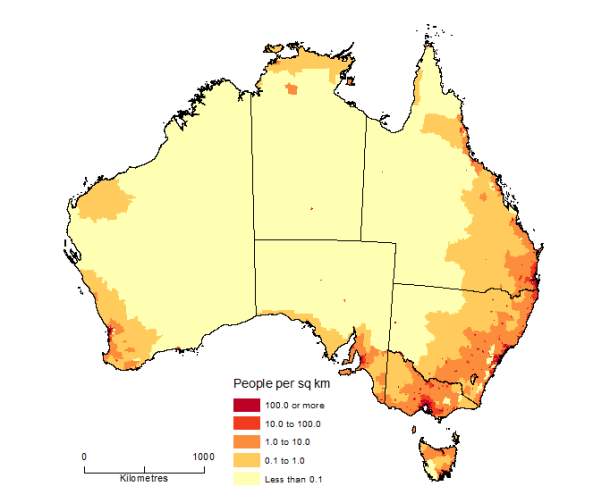
1.3.4 Australia Population Density
Prices start at $10 per page for undergrad work and go up to $21 for advanced levels, depending on urgency and any extras you toss in. Deadlines range from a lightning-fast 3 hours to a chill 14 days—plenty of wiggle room there! Plus, if you’re ordering big, you’ll snag 5-10% off, making it easier on your wallet while still getting top-notch quality.
1.4 Past & Current Infrastructure
Nope—your secret’s locked down tight. We encrypt all your data with top-tier security, and every paper’s crafted fresh just for you, run through originality checks to prove it’s one-of-a-kind. No one—professors, classmates, or anyone—will ever know you teamed up with us, guaranteed.
3.2 Core Network Topology Design
Not even a little—our writers are real-deal experts with degrees, crafting every paper by hand with care and know-how. No AI shortcuts here; it’s all human skill, backed by thorough research and double-checked for uniqueness. You’re getting authentic work that stands out for all the right reasons.
3.2.2 Advantages & Disadvantages of Core Network Design
3.3.1 Advantages & Disadvantages of Aggregation Network Design
Our writers are Ph.D.-level pros who live for nailing the details—think deep research and razor-sharp arguments. We pair that with top plagiarism tools, free revisions to tweak anything you need, and fast turnarounds that don’t skimp on quality. Your research paper won’t just shine—it’ll set the bar.
3.4 Aggregation Network Topology Diagram
You’re in good hands with degree-holding pros—many rocking Master’s or higher—who’ve crushed our tough vetting tests in writing and their fields. They’re your partners in this, hitting tight deadlines and academic standards with ease, all while tailoring every essay to your exact needs. No matter the topic, they’ve got the chops to make it stellar.
4.1.1 High Density Residential Areas
4.1.2 Advantages & Disadvantages of HDRA Technology
4.1.3 High Density Residential Areas Network Diagram
100%—we promise! Every paper’s written fresh from scratch—no AI, no copying—just solid research and proper citations from our expert writers. You can even request a plagiarism report to see it’s 95%+ unique, giving you total confidence it’s submission-ready and one-of-a-kind.
4.1.4 High Density Business Areas
4.1.2 Advantages & Disadvantages of HDBA Technology
4.1.5 High Density Business Areas Network Diagram
Yep—APA, Turabian, IEEE, Chicago, MLA, whatever you throw at us! Our writers nail every detail of your chosen style, matching your guidelines down to the last comma and period. It’s all about making sure your paper fits academic expectations perfectly, no sweat.
4.2.1 Low Density Residential/Business Areas
4.2.2 Advantages & Disadvantages of WiMAX Technology
4.2.3 Low Density Residential/Business Areas Network Diagram
Absolutely—life happens, and we’re flexible! Chat with your writer anytime through our system to update details, tweak the focus, or add new requirements, and they’ll pivot fast to keep your paper on point. It’s all about making sure the final draft is exactly what you need, no stress involved.
4.3.2 Advantages & Disadvantages of Satellite: VSAT Technology
4.3.3 Remote Populated Areas Network Diagram
It’s super easy—order online with a few clicks, then track progress with drafts as your writer works their magic. Once it’s done, download it from your account, give it a once-over, and release payment only when you’re thrilled with the result. It’s fast, affordable, and built with students like you in mind!
We can crank out a killer paper in 24 hours—quality locked in, no shortcuts. Just set your deadline when you order, and our pros will hustle to deliver, even if you’re racing the clock. Perfect for those last-minute crunches without compromising on the good stuff.
6.0 Service and Network Management
6.1 Simple Network Management Protocol
From Internet of Things to internet of every thing
For sure! Our writers with advanced degrees dive into any topic—think quantum physics or medieval lit—with deep research and clear, sharp writing. They’ll tailor it to your academic level, ensuring it’s thorough yet easy to follow, no matter how tricky the subject gets.
Australians accessing online video and audio content, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Social media use, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Use of communications apps, by activity, June 2017(percentage)
Use of communications apps, by activity and age, June 2017 (percentage)
We stick to your rubric like glue—nailing the structure, depth, and tone your professor wants—then polish it with edits for that extra shine. Our writers know what profs look for, and we double-check every detail to make sure it’s submission-ready and grade-worthy.
This project will assist in developing a high-level, end-to-end design of a national next generation telecommunications networks, which will serve all major cities and regional areas of Australia. The reasons why we are upgrading our infrastructure is to keep up with the demands as network usage is constantly increasing, but also to provide a more stable network as reliability is vital but most important for a more secure network, as we want to perform our tasks knowing our data is secure.
Telecommunications and ICTs have been acknowledged as a driver of economic and social development, reducing poverty and creating wealth. This development creates a chance to encourage exchange and monetary advancement by and large, and also business improvement and employment creation, particularly for entrusted populations such as indigenous people groups and people with incapacities.
Send us your draft and tell us your goals—we’ll refine it, tightening arguments and boosting clarity while keeping your unique voice intact. Our editors work fast, delivering pro-level results that make your paper pop, whether it’s a light touch-up or a deeper rework.
Infrastructure is essential to accomplishing the objective of digital incorporation, sustainable and cost-effective in order to provide access to ICTs and services for everyone. The ICT sector is described by fast technology change and by combination of innovative stages for telecommunications, information transportation, distribution and computing. The arrangement of regular system foundations for various telecommunication services and applications and the advancement to all IP-based remote and wired cutting edge systems – grants new opportunities, however these opportunities are surrounded by difficult challenges.
Building up telecommunication infrastructure, Australia has invested heavily in PSTN technology and PLMN networks which are presently facing huge challenges in terms of migration from their existing technology to cutting edge systems networks such as NBN. To overcome these challenges, taking in consideration multiple factors such as the cost related, resources and most important the knowledge to plan for a smooth migration to NGN and QoS for those high date consumptions media services.
Migrating from Australia current infrastructure to an NGN platform requires in taking multiple factors in consideration and planning every aspect carefully such as the core and access network levels. The access network is one of the key parts in giving broadband services, which has the capability of turning into a genuine bottleneck for the conveyance of interactive media applications. It is perceived that the access network is a standout amongst the costliest segments of telecommunication infrastructure contrasted with different parts of the network.
The access network, thus, must to be agreed when examining the status of a telecommunication network foundation for development toward NGN. Without real access network orchestrating, it would challenge for an NGN implementation strategy to succeed. In this way, the access network is one of the essential focus domains in migration to NGN.
The requirement for development of NGN in rural regions is self-evident, as a huge extent of the populace, live in rural regions which have requirements that involved the access of ICT.
Considering these areas when implementing the NGN is hugely important as most of the populace living in rural regions, having low education levels, require sight and sound services to encourage simple access to relevant information and services.
Yes—we’ve got your back! We’ll brainstorm fresh, workable ideas tailored to your assignment, picking ones that spark interest and fit the scope. You choose the winner, and we’ll turn it into a standout paper that’s all yours.
NGN is viewed as a social infrastructure on which broadband services can be given, opening new open doors in the telecommunication business. Nations can profit by NGN arrangement with an extensive variety of cutting-edge ICT-based services and applications in building the information society; implementing systems for the public security and catastrophe alleviation amid crisis communication, particularly early cautioning frameworks for spread of crisis information; and, enhancing access to information and learning in the rural regions and engaging underestimated networks for digital consideration.
• Unrestricted access to service providers: Regardless of which service provide you choose, they will all go through NGN infrastructure cutting down installation cost when switching providers.
A major point to take into considering is the geographic and demographic of Australia to calculate our target audience but also to take into consideration future expansion. Without this information can leave to significant errors even the failure of the entire project. As of now the estimated current population of Australia is around 24,843,333. The population density in around 3 per km2 (8 people per mi2). The total land area is 7,682,300 Km2 (2,966,151 sq. miles). 90.0 % of the population is urban (22,301,673 people in 2018). The median age in Australia is 37.5 years.
| Year | Population | Yearly Change | Migrant (net) | Median Age | Fertility Rate | Density (P/Km²) | Urban Population | ||
| % | Total | % | Total | ||||||
| 2018 | 24,772,247 | 1.32 | 321,686 | 169,993 | 37.5 | 1.87 | 3 | 88.8 | 22,301,673 |
| 2017 | 24,450,561 | 1.35 | 324,713 | 169,993 | 37.5 | 1.87 | 3 | 90.0 | 21,996,082 |
| 2016 | 24,125,848 | 1.37 | 326,292 | 169,993 | 37.5 | 1.87 | 3 | 89.9 | 21,692,663 |
| 2015 | 23,799,556 | 1.47 | 335,898 | 182,621 | 37.4 | 1.89 | 3 | 89.9 | 21,392,649 |
| Year | Population | Yearly Change | Migrant (net) | Median Age | Fertility Rate | Density (P/Km²) | Urban Population | ||
| % | Total | % | Total | ||||||
| 2020 | 25,398,177 | 1.31 | 319,724 | 169,993 | 37.9 | 1.83 | 3 | 90.2 | 22,910,275 |
| 2025 | 26,857,068 | 1.12 | 291,778 | 150,000 | 38.9 | 1.80 | 3 | 90.9 | 24,400,230 |
| 2030 | 28,234,742 | 1.01 | 275,535 | 150,000 | 39.8 | 1.78 | 4 | 91.5 | 25,834,777 |
| 2035 | 29,526,448 | 0.90 | 258,341 | 150,000 | 40.6 | 1.77 | 4 | 92.2 | 27,222,968 |
| State | Population (m) |
| New South Wales | 7.3 |
| Victoria | 6.0 |
| Queensland | 4.4 |
| South Australia | 1.3 |
| Western Australia | 2.2 |
| Tasmania | 0.5 |
| Northern Territory | 0.2 |
| Australian Capital Territory | 0.4 |
| Australia | 22.3 |













 1.4 Past & Current Infrastructure
1.4 Past & Current InfrastructureApplication
Service Control
Transport
Yep—need changes fast? We’ll jump on your paper and polish it up in hours, fixing whatever needs tweaking so it’s ready to submit with zero stress. Just let us know what’s off, and we’ll make it right, pronto.
Access
End Points
The next generation network will grant broadband connectivity across the entire country regardless of the technology or locations. As the center technology or should we say the Aggregator will be IP over DWDM, which is utilized to connect the various access technology that the service provides have to offer/available. Using Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), will guarantee the separated Quality of Service (QOS) for each network/s. The network is separated into three main layers which are; Core, Aggregation, and Access networks.
The responsibilities for each layer are as follow:
All of these proposed access technologies has a service layer allowing connectivity and simplicity to manage. The network design diagram is separated based upon the layered architecture.
Core Network Layer: This is the central/backbone of the network. Its core functionality is to provide communication across different access technology but also to provide communication across external existing networks.
Sure thing! We’ll whip up a clear outline to map out your paper’s flow—key points, structure, all of it—so you can sign off before we dive in. It’s a handy way to keep everything aligned with your vision from the start.
Access Network Layer: The access layer is responsible for connecting users to their immediate service providers. First the communications start by enabling users to communicate with the communication system to allow the start information exchange/transmission. These communications can either be wired and wireless or broadband and narrowband. The below technologies have been chosen to implement within our design:
Aggregation Network: Is the responsible technology to connect multiple network access networks and provide connectivity by being connected to the Core Network. In terms of telecommunication network, the aggregation network is commonly placed between the core layer and access layer, so it can extend the reachability of the core network to the access layer network. The technologies used in the Aggregation varies on multiple factors such as the core and access layer, coverage area and geographical state.
Today telecommunication technology is speared into four major technology of communication – Voice Telephone, Internet, Cable TV, Mobile Networks. These communications systems will soon not have the capacity to keep up with the demand and will need a develop a new form of technology that will keep up with the current and future demands. The demands are increasing significant because of the new data-consuming services around us such as: cloud computing, high volume of data, high definition videos, quality voice calls, video broadcasting and many more high-quality-data-consuming services.
With the demand of rich services such as video, data and voice many organizations required a network infrastructure that can carry out all these services without difficulties, this is when NGN comes in and evolves the world.
Security is an important factor take into consideration. As the rise of cybersecurity increases and the demand for cybersecurity roles increase world-wide, making everyone’s data secured is extremely vital. NGN will provide advanced intrusion detecting systems, defense for denial-of-services, will monitor and log all traffic, whilst implementing firewall to add an extra layer of security. As we also come to the new era of technology known as Artificial Intelligence this will decrease significant cyber-crime or even stop it as machines will be able to think by themselves without human interaction.
Apart from security, many more benefits are associated with the implementation of NGN such as:
Our next generation network in made up of IP/MPLS technology. Multi-Protocol Label Switching is a technique that involves in creating a path for routing packets. It operates in the Layer 2.5 and works with Layer 2 & 3 of the OSI Model. The way label switching works on MPLS is the first devices does a routing lookup searching for the final destination router, it then pre-determined the path from the current location to the final router. IP/MPLS routing layers can be utilized to achieve two main functions; Provider Edge routing & Provider routing, which chains all the IP services that are linked from the client and the MPLS is utilized to route the packets/segments towards their final destination address.
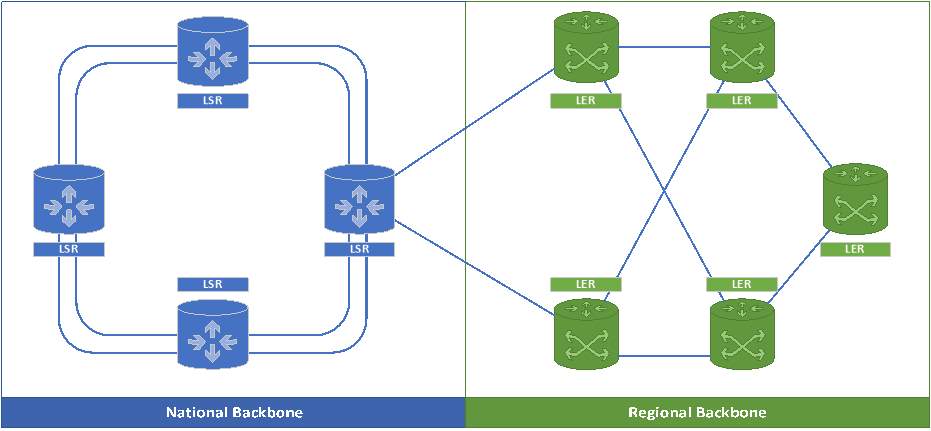
In our proposed design, the core router is connected to 3 other core routers in the national backbone under the ring topology. In terms of the regional backbone it is connected in a mesh topology. Optic fiber cables are used to connect the core router in order to achieve the highest speeds, but also to achieve QoS. Most important redundancy is taken into consideration as if one of these routers fails, we have alternativity core routers adapting immediately in case any router fails.
Absolutely—we’ll weave in sharp analysis or eye-catching visuals like stats and charts to level up your paper. Whether it’s crunching numbers or designing a graph, our writers make it professional and impactful, tailored to your topic.
When talking about national backbone, we must also take into consideration multiple factors, to guaranteed QoS but also 100% availability. The national backbone is corrected in a ring topology with not 1 but 2 double connections using the super-fast high-speed fiber cable between each router to guarantee/support availability at all times and resiliency. In the situation that any link fails, the topology is design in such way that it would use the second connections to continue running the service simultaneously.
In terms of the regional backbone network, our design uses a meshed topology based on multiple reasons. The meshed topology was chosen due to the fact that we want to ensure that all the routers have multiple points of connections, and would be using the chosen topology due to the difficulty in implementing but also the cost associated with it.
The advantages & disadvantages of MPLS are as follow:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
This is the network layer that is responsible for providing communication from the Access Layer to the Core Layer by extending it Core Layer functions through the Access layer. This allows the aggregation layers to operate between Layer 1 & 2. The core functionalities of this layers is the availability, fast switching, scaling is extended to this layer as demonstrated in the diagram below.
The LER router which acts as the Edge router is connected to numerous aggregation routers. In our aggregation diagram we are using ROADMs which stands for Reconfigurable ADD-Drop Multiplexer, which are the programmed form of Optical ADD-Drop Multiplexer. Using ROADMs allows our network to avoid the conversion of optical to electrical signal and vice versa meaning faster network. ROADM’s have many benefits and are not limited to providing broadband service to the end user in the situation that the Access Technology fails, which is extremely unlikely due to the strategic of redundancy we have in place. A single Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) ring can be utilized to connect numerous Access technology. Depending on population, geographical location and numbers of user we can determine how many ROADM’s we need to implement.
Below is a list of advantages within the aggregation network layer:
We tackle each chunk with precision, keeping quality consistent and deadlines on track from start to finish. Whether it’s a dissertation or a multi-part essay, we stay in sync with you, delivering top-notch work every step of the way.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
In terms on how Australia is connected to the Internet is by the rest of the world high-speed submarine optical cable. These cables land at Alexandria and Paddington (NSW) and Perth (WA). As a result, we are required to install 7 core backbone networks at the following locations.
Yes—we’ve got it down! Our writers switch seamlessly between UK, US, Australian, or any other standards, matching your school’s exact expectations. Your paper will feel native to your system, polished and ready for wherever you’re studying.
As New South Wales carries the largest population in Australia and also carries the submarine optical cable, it would be best practice to have an additional backbone to act as a gateway for the international traffic.
In terms of the regional infrastructure it will remain the same, however in terms of the LER technology it depends upon numerous factors such as the number of users and bandwidth in demand by the users.
The Access network is responsible for connecting users to the immediate service provider. The Access network is separated into three main categories:
In our design we use all three to provide access solution across the entire country.
We have two versions of Access network designs for the High Density Residentials areas. These proposed designed varies on the current infrastructure in ways such as:
Progressive delivery is a cool option where we send your paper in chunks—perfect for big projects like theses or dissertations. You can even pay for it in installments. It’s just 10% extra on your order price, but the perks are worth it. You’ll stay in closer touch with your writer and can give feedback on each part before they move to the next. That way, you’re in the driver’s seat, making sure everything lines up with what you need. It saves time too—your writer can tweak things based on your notes without having to redo huge sections later.
Fiber to the Node (FTTN) connection is used in situations where there is an existing copper line to the premises whilst providing optic fiber cable to the cabinet which is commonly <500m away from the customer premises.
FTTN uses VDSL2 modem to transmit data over the copper line. In terms of the bandwidth speed it varies on the distance from the node to the premises. Download speeds of 100Mbps can be achieved by having the node 400m away and speed of up 60Mpbs if the node is more than 700m from the cabinet. These speeds can be altered also by the bandwidth package that the user chooses from the ISP, hence does not guaranteed the speeds at 100%. We must also be mindful that speed may vary depending on the distance from the cabinet, and the quality of the links used.
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) can be implemented with the help of Passive Optical Network (PON) as it brings the fiber cabling and signals all way to the premises. This is achieved by using an Optical Splitter which is responsible for distributing the signal. In order for this technology to be functioning and implemented correctly, we must ensure total distance from the exchange to the customer locations (<20Km). This technology is shared as it is point-to-multiple-point network which means all users sharing the bandwidth. Being mindful of congestion is vital when implementing this technology. PON’s can share across 32 subscribers and is the most cost effective and fasted method for these sorts of areas.
The advantages and disadvantages of FTTN are:
Absolutely! If your teacher’s got feedback, you can request a free revision within 7 days of approving your paper—just hit the revision request button on your personal order page. Want a different writer to take a crack at it? You can ask for that too, though we might need an extra 12 hours to line someone up. After that 7-day window, free revisions wrap up, but you can still go for a paid minor or major revision (details are on your order page). What if I’m not satisfied with my order? If your paper needs some tweaks, you’ve got that free 7-day revision window after approval—just use the “Revision” button on your page. Once those 7 days are up, paid revision options kick in, and the cost depends on how much needs fixing. Chat with our support team to figure out the best way forward. If you feel the writer missed the mark on your instructions and the quality’s off, let us know—we’ll dig in and sort it out. If revisions don’t cut it, you can ask for a refund. Our dispute team will look into it and figure out what we can offer. Check out our money-back guarantee page for the full scoop.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
The advantages and disadvantages of FTTH are:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
We also have two versions of Access network designs for the High Density Business areas such as:
The advantages and disadvantages for HDBA are as follow:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
In terms of providing connectivity to the Low Density Residentials/Business areas we proposed in deploying WiMAX. We chose this technology due to multiple reasons, the main reason is the cost, it is too high to deploy optic fiber in low population areas as the return investment isn’t there.
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access is a wireless broadband technology similar to WiFi but at a much higher speed over great distances and for greater number of users. It works by pointing out a line-of-sign to other WiMax transmitters to provide connectivity around the designated area. It is based on IEEE 802.16 wireless broadband standard.
The advantages and disadvantages for HDBA are as follow:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
In terms of providing connectivity to the Remote Rural areas we proposed in deploying Satellites. Figuring out what technology to deploy in this unpopulated was extremely complex as cost needs to be carefully considered but also the future growth of the geographical area. A key point to consider is the returned investment, as regardless what technology we use, we would face a loss.
After careful consideration, we decided to deploy Satellite using VSAT system. VSAT stands for Very Small-Aperture Transceiver, which contains numerous earth stations in order to achieve two-way communication with a Master Earth Station through geostationary satellites. We would also be deploying a Mesh Topology due to its single hop functions and redundancy options.
The Geostationary satellites are located in the equator and orbit every 24 hours hence it appears stationary to anyone observing. Each satellite can come 120 degrees, making up 3 geostationary satellites to cover the entire Earth.
The advantages and disadvantages for HDBA are as follow:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Providing a high-speed wireless internet solution for the entire population of Australia for the wireless mobile devices is vital to ensure that end-users can also access their services on the go. In this proposed design the type of mobile network we decided to deploy is 3GPP 4G, due to numerous reasons, but mainly because it can provide Quality of service. The 4G network uses LTE technology, however it has evolved to LTE -Advanced Pro which can support over 1Gbps. The 4G networks is made up of numerous components such as:
Quality of Service is more important now than 5 years ago, due to the demands of the public but also due to the new inventions and advancements of technology. As IoT and watching videos are the main two growing factors, companies like Netflix, Spotify, Optus Sport are mainly responsible for this growth of demand. Live sport is also extremely responsible for the growth of video content, specially on portable devices that support numerous platforms for these services to be accessed on.
We gathered this data of demand from the annual Australian Communications and Media Authority Communication Report 2016-17 which key points are summarised in the Appendix section, which offers a graphical diagram outlining the demands of each service and target audience.
In simple form what Quality of Service is the mechanism that is used to control delays, bandwidth and packet loss in the network to ensure that you’re constantly getting quality, fast, reliable service. Below are the key features of QoS:
Differentiated Service also known as DiffServ Model is a framework that can manage different quality of services. Its functionality is to mark packets headers using the ToS byte by marking the first 3 bits with IP Precedence and 6 bits with IP DSCP. The value of the IP Precedence is part of the IP DSCP value though it is design not be same concurrently. IP DSCPT is compatible with the IP precedence bits due to its backward compatibility mechanism. IP Precedence has a maximum of 8 different IP precedence markings whilst IP DSCP has a maximum of 64 DSCP markings. These 8 values for IP Precedence are defined based on priority as 0 = Lowest to 7 = Highest priority.
Simple Network Management Protocol also known as SNMP is used to manage IP objects on an IP-based network. Its simple mechanism of poll/response where an SNMP server gathers information from sending poll request to the Management Information Base (MID) and waits for the response from the node.
The SNMP in made up of 3 versions; v1, v2c, v3. In this design we will be using version 3 as it supports MD5 or SHA encryptions guaranteeing your privacy and encryption using DES algorithm.
Remote Monitoring (RMON) is a standard monitoring technique allowing networks monitors and console system to exchange information.
“The RMON MIB added much needed remote monitoring capability to the basic SNMP MIB; it allowed the network manager to view a LAN segment as a whole rather than as a collection of individual devices. [20]
Devices with the RMON MIB implemented behave like a network probe; passively recording traffic information that can in turn be retrieved via SNMP GET commands. [20]“
All information for this section was copied from Australian Communications and Media Authority -Communication Report 2016-17. [16]
“The mobile phone is now the most popular and most frequently used device to go online. The shift to mobile phone-only for communication continues, with 6.67 million Australian adults having a mobile phone and no fixed-line telephone at home. The popularity of communications apps on mobile phones has also continued, with eight in 10 internet users having used an app to communicate.
Content use and, more specifically, demand for video content over the internet, is increasing, with 59 per cent of Australians having watched content online at June 2017. Service providers are responding by expanding platforms and services to meet their customers’ online needs. Australians continue to spend a majority of their viewing time watching broadcast television.”
The IoT is moving mainstream. The year to June 2017 saws Australia’s telecommunications carriers makes firm commitments for network investments, technology trials and commercial deployments of IoT. Telstra announced plans to build a national IoT network in partnership with Ericsson. Vodafone completed a successful trial of Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) technology with utilities and technology partners, with plans to launch commercial services in Melbourne late in 2017. Optus completed its NB-IoT trial early in 2017 (a date for the launch of its services had not been announced at the time of publication).
The adoption of the IoT in Australia has grown rapidly, with the technology embraced across industries and locations—from smart bins in Bondi to monitoring water tanks on rural properties. Consumers have also adopted IoT technology, with an increased proportion of Australian adults connecting smart TVs to go online within the home.
Industry forecasts indicate that 29 billion devices will be connected worldwide by 2022, of which 18 billion will relate to IoT.
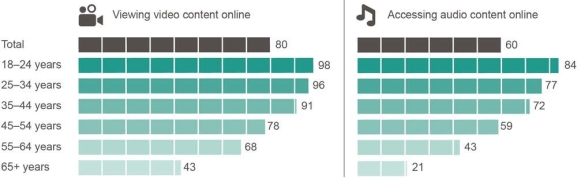 Australians accessing online video and audio content, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Australians accessing online video and audio content, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Base: Australians aged 18 and over who accessed the internet.
Note: ‘Don’t know’ and ‘Prefer not to say’ responses are excluded from analysis. Source: ACMA-commissioned survey, June 2017.
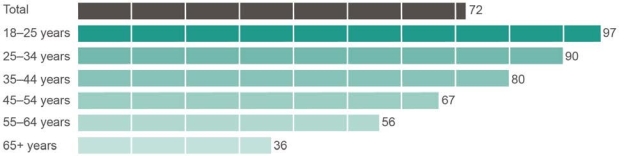 Social media use, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Social media use, by age, June 2017 (percentage)
Base: Australians aged 18 and over who accessed the internet.
Note: ‘Don’t know’ and ‘Prefer not to say’ responses are excluded from analysis. Source: ACMA-commissioned survey, June 2017. “
At June 2017, 88 per cent of Australian internet users had used an app to communicate via messages or voice or video calls in the last six months—using apps to send messages was the most popular (85 per cent). Just over four in 10 (42 per cent) did all three.
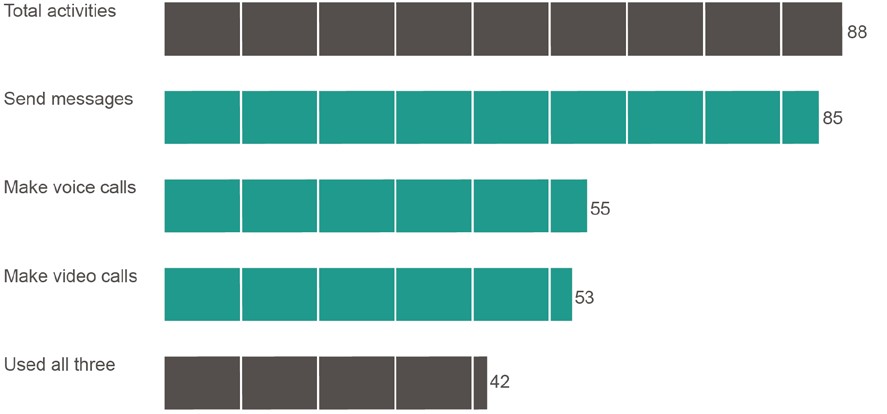
Base: Australians aged 18 and over who accessed the internet.
Note: ‘Don’t know’ and ‘Prefer not to say’ responses are excluded from analysis. Source: ACMA-commissioned survey, June 2017.
Younger Australians were the most active users of communications apps, with 98 per cent of those aged 18–24 using an app to send messages (Figure 2.12). There was also high use among those aged 25–34 (95 per cent) and 35–44 year olds (88 per cent), dropping to 61 per cent for those aged 65 and over.
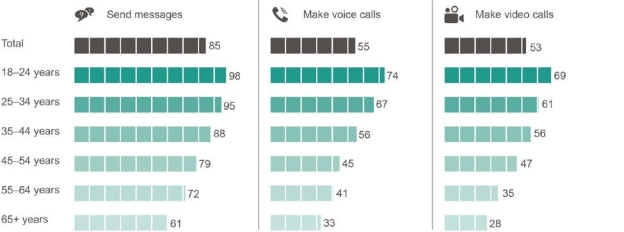 Use of communications apps, by activity and age, June 2017 (percentage)
Use of communications apps, by activity and age, June 2017 (percentage)Base: Australians aged 18 and over who accessed the internet.
Note: ‘Don’t know’ and ‘Prefer not to say’ responses are excluded from analysis. Source: ACMA-commissioned survey, June 2017.
“
In this Next Generation Telecommunication Design for the Australian Communication Network, we proposed and designed a network that can provide Internet solutions regardless of the location or device through taking numerous factors into consideration such as;
All these requirements are vital in order to determined what technology must be used, but also the quantity. Scalability and QoS is also an important factor as what are the point of having a network when it’s not reliable.
Overall, we covered the Design Overview which outlines the entire network diagram in a brief form whilst outlining the benefits associated for the entire design. We also cover the Core Layer & Access Layer technologies, its pros and cons, network diagram which enables us to have a detailed fundamental understanding of the deployment.
We divided the Access layer into 4 categories; Wired Access, Wireless Access, Remote Areas, Mobile Wireless Access which all provide different type of technology, whilst all operating together in order to provide connectivity through the Aggregation layer.
Quality of Service and Service and Network Management is also outlined in this report, to ensure the quality of the service is achieved whilst managing the network accordingly through the implementation of Remote Access.
Through this design, we can achieve a reliable, scalable, quality telecommunication design, that will cover the demand for the entire of Australia but also for the future growth of Australia.
[1] Worldometers.info. (2018). Australia Population (2018) – Worldometers. [online] Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/australia-population/ [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[2] 9tut.com. (2018). CCNA Training. [online] Available at: https://www.9tut.com/ [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[3] SearchNetworking. (2018). Core, Distribution and Access. [online] Available at: https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/tip/Core-Distribution-and-Access [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[4] Don Jacob, T. (2018). A Quick Start To MPLS Fundamentals | Packet Design. [online] Packet Design. Available at: https://www.packetdesign.com/blog/quick-start-mpls-fundamentals/ [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[5] Aussiebroadband.com.au. (2018). FTTP vs FTTN vs FTTC: Connections to the National Broadband Network explained | Aussie Broadband. [online] Available at: https://www.aussiebroadband.com.au/blog/fttp-vs-fttn-connections-national-broadband-network-explained/ [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[6] Garden, H. (2018). How WiMAX Works. [online] HowStuffWorks. Available at: https://computer.howstuffworks.com/wimax1.htm [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[7] King, J. (2018). Key features of Next Generation Networks. [online] Bigair.com.au. Available at: https://www.bigair.com.au/blog/key-features-of-next-generation-networks [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[8] Whistleout.com.au. (2018). NBN Fibre to the Premises: Everything you need to know. [online] Available at: https://www.whistleout.com.au/Broadband/Guides/nbn-fttp-everything-you-need-to-know [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[9] Slideshare.net. (2018). NGN Next Generation Network. [online] Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/HavarBathaee/ngn-nextgeneration20network [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[10] En.wikipedia.org. (2018). Satellite link. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satellite_link [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[11] Scutt, D. (2018). This map shows population density across Australia. [online] Business Insider Australia. Available at: https://www.businessinsider.com.au/this-map-shows-population-density-across-australia-2017-7 [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[12] Google.com. (2018). simpson desert on a map – Google Search. [online] Available at: https://www.google.com/search?sa=G&hl=en-AU&q=simpson+desert+on+a+map&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:CAQSlwEJMgj0lpIzAlwaiwELEKjU2AQaBAgVCAsMCxCwjKcIGmIKYAgDEijBB9YI_1RLYCcYHvwfNB8IHxQfRApY57z7oP-c_15T_1kP6Ir4z_1uPvI-GjCs8_1r-3dqTPMUU6qCkQAYFFJbRwE8Ax2lFDmVOYO2oQacSoWfTFYe6J6vtQFGOCjcgBAwLEI6u_1ggaCgoICAESBHbMXeYM,isz:l&ved=0ahUKEwjj48X_yYfeAhUCa94KHd7PDJYQ2A4ILigE&biw=2144&bih=1054#imgrc=D0tGzThPwyqz4M: [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[13] SearchTelecom. (2018). What is dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM)? – Definition from WhatIs.com. [online] Available at: https://searchtelecom.techtarget.com/definition/dense-wavelength-division-multiplexing [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[14] SearchNetworking. (2018). What is Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)? – Definition from WhatIs.com. [online] Available at: https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/Multiprotocol-Label-Switching-MPLS [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[15] White, G. (2018). How Do Packets Get Around? | Understanding Networks and TCP/IP | InformIT. [online] Informit.com. Available at: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=131034&seqNum=5 [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[16] Acma.gov.au. (2018). Australian Communication Report 2016-17. [online] Available at: https://www.acma.gov.au/-/media/Research-and-Analysis/Report/pdf/Communications-report-2016-17-pdf.pdf?la=en [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[17] En.wikipedia.org. (2018). Differentiated services. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differentiated_services [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[18] The Pros and Cons of WiMAX. [online] Tom’s Guide. Available at: https://www.tomsguide.com/us/the-pros-and-cons-of-wimax,review-398.html [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[19] Schriber, A. (2018). VSAT Defined: What is it and How Does It Work?. [online] Internet Access Guide. Available at: http://internet-access-guide.com/vsat-defined-what-is-it-and-how-does-it-work/ [Accessed 15 Oct. 2018].
[20] Icanovich, M. n.d., “HET729 Design and Management of Networks, Network Management”
Tags: Affordable Academic Writing Services USA, Assignment Help for Master's Students, Online Class and Exam Help, Thesis and Dissertation Writing UKYou Want The Best Grades and That’s What We Deliver
Our top essay writers are handpicked for their degree qualification, talent and freelance know-how. Each one brings deep expertise in their chosen subjects and a solid track record in academic writing.
We offer the lowest possible pricing for each research paper while still providing the best writers;no compromise on quality. Our costs are fair and reasonable to college students compared to other custom writing services.
You’ll never get a paper from us with plagiarism or that robotic AI feel. We carefully research, write, cite and check every final draft before sending it your way.